Der Spezialist im Bereich der Ökonometrie!
EViews bietet Finanzinstituten, Unternehmen, Regierungsbehörden und MitarbeiterInnen aus akademischen Einrichtungen Zugriff auf leistungsstarke Statistik-, Zeitreihen-, Prognose- und Modellierungstools über ein innovatives, benutzerfreundliches objektorientiertes Interface.
Mit EViews können Sie Ihre Daten schnell und effizient verwalten, ökonometrische und statistische Analysen durchführen, Vorhersagen oder Modellsimulationen erstellen und Grafiken und Tabellen von hoher Qualität für die Veröffentlichung oder Aufnahme in andere Anwendungen erstellen.
Zusätzlich bietet EViews Ihnen ein elegantes und schnelles Handling von Zeitreihen unterschiedlicher Granularität. EViews beinhaltet fast alle etablierten Schätzmodelle (LS, 2SLS, GLM, etc.), sowie alle klassischen Modelle (ARIMA, ARCH, GARCH, etc.) und eröffnet Ihnen vielfältige Möglichkeiten zur Simulation von Szenarien (Monte Carlo Simulationen etc.).
Finden Sie selbst heraus, warum EViews der weltweit führende Anbieter von Windows-basierter ökonometrischer Software und die erste Wahl für diejenigen ist, die das Allerbeste verlangen.
- Intuitives, einfach zu bedienendes User Interface
- Mächtiges Analysewerkzeug
- Hochentwickeltes Datenmanagement
- Präsentationsfertiges Output
- Klassische Kommandozeilen und Programmier-Interface
Schauen Sie sich die Neuerungen im Herstellervideo am Beispiel von Bayesian Time-Varying Coefficient VAR an:
Die neue Version von EViews ist noch leitstungsstärker und benutzerfreundlicher geworden. Hier nun einige der Neuerungen:
- Enhanced ARDL and NARDL estimation.
- Improved Pool Mean Group (PMG) estimation.
- Difference-in-Difference estimation.
- Bayesian Time-varying Coefficient VARs.
- Enahanced VEC estimation.
- Improved cointegration testing.
- New ARDL and PMG diagnostics.
- Panel Cluster Standard Errors.
- Daily seasonal adjustment.
- Alternative graphical user interface.
- Program debugging tools.
- Run/program EViews in a Jupyter Notebook.
- Graph improvements.
- Table improvements.
- New Excel writing engine.
Und mehr!!
Die wichtigsten Tools von EViews auf einen Blick:
- Zeitreihen- und Panelanalysen
- Monte Carlo Simulationen und Forcasting
- Datenmanagement: Automatische Anpassung von Daten unterschiedlicher Granularität, Unterstützung verschiedenener Datei-Formate (xls, xlsx, csv, u.m.), Schnittstellen zu weiteren Statistik Programmen (R, MATLAB, etc.), Anbindung zu unterschiedlichen Datenbanken (FRED Datenbank, ...)
- Glatte Schwellenregression (STR und STAR)
- Strukturelle VAR-Beschränkungsverbesserungen
- Neue saisonale Anpassungsmethoden
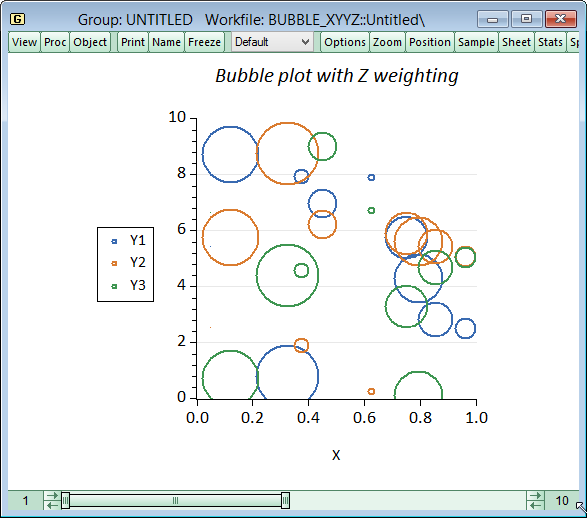
- Neue Charting-Tools, einschließlich Bubble-Plots
- Automatisches Backup- und Datenverlaufssystem
- Verbesserte R-Integration
- Konnektivität mit Weltbank, Eurostat und anderen
- Einsparung als Tableau®
Dies könnte Sie auch interessieren
Stata BE
Stata SE
Stata MP
EViews
Prognosesoftware im Bereich der Ökonometrie
EViews stellt Forschern, Firmen, Ämtern und Studenten mächtige Statistik-, Vorhersage- und Modellierungswerkzeuge, basierend auf einer innovativen, leicht zu bedienenden, objektorientierten grafischen Benutzerschnittstelle zur Verfügung. Die Kombination von Leistungsfähigkeit und einfacher Bedienung machen EViews zu der Anwendung für alle, die mit Zeitreihen, Querschnitts- oder Längsschnittdaten arbeiten. Mit EViews verarbeiten sie schnell und effizient Ihre Daten, führen ökonometrische und statistische Analysen durch, generieren Vorhersagen oder Modellsimulationen und produzieren qualitativ hochwertige Graphen und Tabellen für Publikationen oder Ausgaben für andere Applikationen - per Mausklick und ohne komplizierte Kommandos!
Unterschied zwischen Enterprise und Standard Edition
EViews wird in zwei Editionen angeboten: Standard und Enterprise. Die Enterprise Edition beinhaltet alle Features der Standard Edition und bietet darüber hinaus noch weitere Vorteile:
- Datenbankanbindung
Dank ODBC können Sie selbst große externe Datenbanksysteme wie z.B. Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM DB2 oder Sybase mit EViews verbinden und so Ihre Daten bequem auswerten. Oder nutzen Sie die EViews Schnittstellen EDX (Database Extension Interface) und EDO (EViews Database Object) und erstellen Sie maßgeschneiderte Anbindungen zu proprietären Datenquellen. Das Arbeiten mit umfangreichen Datenbanken wird erheblich erleichtert. - Datenquellen von Drittanbietern
Mit der Enterprise Edition können Sie direkt und in Echtzeit Daten von Drittanbietern erhalten, durchsuchen und direkt in Ihre Workfiles einbinden. Unterstützt werden hierbei Datenbanksysteme wie z.B. Bloomberg, IHS Economics, FactSet und mehr.
EViews - Grafiken
EViews bietet eine Vielzahl an grafischen Darstellungsformen, die besonders geeignet zur Darstellung von Zeitreihen sind. Damit eignet sich EViews besonders für Forschungsbereiche wie Modellierung von Zinsen und Aktienkursen (bzw. Finanzmarktdaten im Allgemeinen), Unternehmensanalyse, Kapitalmarktanalysen oder auch für das Portfolio Management.
In EViews stehen unter anderem Liniendiagramme, Balkendiagramme, Tortendiagramme, Scatterplots, gemischte Linien-Balken- Diagramme und Box-Plots zur Verfügung. Mit zahlreichen Einstellungen können mit Hilfe von EViews Linienfarben, Liniendicke, Rahmengestaltung oder auch die Skalierung der Achsen kontrolliert werden. Mit EViews werden Legenden automatisch erstellt. Es ist möglich Notizen in die frei skalierbaren Grafiken an beliebiger Stelle in der Grafik einzufügen. Zu Präsentationszwecken können Sie mit EViews alle möglichen Grafiken beliebig kombinieren.
Das alles kann mittels einfacher Mausklicks in einer übersichtlichen Menüstruktur kontrolliert werden.
Das IHS Global Link Model ist das größte makroökonomische Model auf dem Markt. Erhalten Sie Zugriff zu einer gigantischen Datenbank mit Informationen zu globalen Wirtschaftsleistungen und berechnen Sie in Echtzeit die Trends globaler Wirtschaftsbereiche und deren Einfluss auf Rohstoffpreise, Wechselkurse, Währungs- und Finanzpolitik und vieler weiterer Variablen. Mit der IHS Economic Simulation Engine können Sie Szenarien erstellen und dessen Auswirkungen berechnen lassen. Alle Daten des IHS Global Link Models lassen sich ohne Probleme nach EViews exportieren und von dort aus weiter bearbeiten. Sie haben des Weiteren jederzeit Zugang zu Beratung durch Statistik- und Analyse-Experten von IHS.
Weitere Informationen
- EViews-Homepage (IHS EViews).
- Erweitern Sie die Funktionalität von EViews um zahlreiche frei herunterladbare Add-ins und Library Packages. Download direkt beim EViews-Hersteller IHS EViews in den USA.
Unsere Schulungen zur Software EViews
STATCON bietet Ihnen nicht nur professionelle Statistik Software an, sondern auch professionelle Schulungen zu dieser Software. Unsere Schulungen reichen von kompakten Einführungen in die grundlegenden Funktionen der Software, bis hin zu komplexen Funktionen und zielgerichteten Anwendungsbeispielen. Wir bieten In-house und Off-site Schulungen an. Zusätzlich dazu bieten wir Online-Webinare für bequemes Lernen von zu Hause aus.
EViews - Einführung
Dieser zweitägige Kurs macht sie mit den Grundlagen der Ökonometrie und Zeitreihenanalyse vertraut. Ein besonderer Schwerpunkt liegt auf dem linearen Regressionsmodell als Grundmodell der ökonomischen Modellbildung und auf der Zeitreihenanalyse. Parallel wird die Statistik-Software EViews vorgestellt. Zum Produkt...
EViews - Grundlagen der Programmierung
Dieser eintages Kurs dreht sich ganz um die EViews Skriptsprache. Lernen Sie wie man Routineaufgaben automatisiert oder eigene Methoden für EViews zu entwickeln. Darüber hinaus zeigen wir Ihnen den Umgang mit Datenbanken, Modellen und Verknüpfungen, Objekte und Graphen und vieles mehr. Zum Produkt...
EViews - Modellierung: Komplexe Modelle
Dieser zwei-Tages-Kurs stellt verschiedene fortgeschrittene Modelle für die Modellierung von Zeitreihen vor. Es werden u.a. behandelt; Vektormodelle, etwa den VAR (vector autoregressive) bzw. VEC (vector error correction) Modell. Schließlich behandeln wir noch die ARCH bzw. GARCH Modelle für die Analyse von Finanzmärkten. Zum Produkt...
EViews Webinar - ARCH und GARCH
In diesem 3-stündigen Online-Seminar lernt der Teilnehmer Methoden zur Modellierung und Prognose von Volatilitäten kennen. Dazu werden ARCH- und GARCH-Modelle theoretisch besprochen. Zum Produkt...
EViews Webinar (kostenfrei) - Tipps &Tricks
In unserer Tips & Tricks-Reihe werden wir die Installation und Anwendung von Add-Ins in EViews vorstellen. Dabei werden die Add-Ins zur automatisierten Modellwahl bei ARIMA-Modellen und zur Prognose mit Hilfe von VAR-Modellen benutzt. Zum Produkt...
EViews Software Updates & Patches
Eviews bietet auf ihrer Website Minor-Updates und Patches für die Software EViews in den älteren Versionen an. Dort erhalten Sie ebenfalls Zugriff auf diverse Whitepapers, Datensätze, und Third Party Data Interfaces.
Systemvoraussetzungen für die Software EViews V.13
|
CPU: |
Pentium or better |
|
|
Operating System: |
Windows 11 (64bit) |
Windows 10 (64bit) |
|
Memory: |
512 MB |
|
|
Disk Space: |
400 MB of available hard disk space for the EViews executable, supporting files, full documentation, and example files. |
Funktionen der Software EViews
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Neue Features in EViews 13:
EViews 13 bietet eine Vielzahl spannender Änderungen und Verbesserungen. Nachfolgend finden Sie eine Übersicht über die wichtigsten Neuerungen in Version 13.
EViews Interface and Programming
- Pane and Tab alternative user interface.
- Program Language Debugging.
- Jupyter Notebook Support.
- Program dependency tracking.
Data Handling
- Daily deasonal adjustment.
- Improved Excel writing engine.
- World Health Organisation connectivity
- Trading Economics connectivity
- National statistical bureaus connectivity
- Holiday function improvements
- Miscellaneous Improvements
New Graph, Table and Geomap Features
- Line and Shade Transparency
- Custom Data Labels
- High-low-median Colormap Presets
- Miscellaneous Improvements
Econometrics and Statistics
Estimation
- Non-linear ARDL Estimation
- Improved PMG Estimation
- Difference-in-Difference Estimation
- Improved VEC Estimation
- Bayesian Time-varying Coefficient Vector Autoregression
Testing and Diagnostics
- Cointegration Testing Enhancements
- ARDL Diagnostics
- Pool Mean Group / Panel ARDL Diagnostics
- Enhanced Impulse Response Display
Interessante Funktionen von älteren EViews-Versionen:
EViews Interface
Interactive command explorer to view all the applicable commands for an object and its documentation.
- Name and command auto-complete.
- Value-based spreadsheet and Geomap coloring.
Data Handling
- Integration with Python.
- Duplicates analysis.
- Split-observations high-to-low frequency conversion method.
- Interface to the following data sources
- Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
- US Census.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Graphs, Tables and Spools
- Geographic maps.
- Fan charts.
Econometrics and Statistics
Estimation
- Improved Bayesian VARs.
- Mixed frequency VARs.
- Switching VARs (Markov and simple).
- Elastic net and LASSO machine learning.
- Functional coefficient and localized regression.
- Additional cluster robust standard errors.
Testing and Diagnostics
- Seasonal unit root tests.
- EViews Schnittstelle
Automatischer und benutzergesteuerter Workfile-Verlauf, Schnappschuss und Backup-System,
Live-Statistiken für Tabellenkalkulationen, Unterstützung für lange Objektnamen,
Verbesserte Logging-Fähigkeiten.
- Datenverarbeitung
Verbesserte Integration mit R, Attribute importieren und exportieren, Schnittstelle zu Weltbankdaten, Schnittstelle zu den Vereinten Nationen,
Schnittstelle zu Eurostat-Daten, Schnittstelle zu den Europäischen Zentralbankdaten, Speichern nach Tableau®, Speichern nach JSON.
- Diagramme, Tabellen
Bubble plots, Serienaktualisierung in Graphen, Neue Standard-Grafik-Stile, Neue Grafikoptionen, Tabellensortierung.
Ökonometrie und Statistik
- Berechnungen
Saison-Trend-Zersetzung (STL), MoveReg wöchentliche saisonale Anpassung, Spezielle Funktionsberechnung.
- Schätzung
Glatte Schwellenregression (STR), Heteroskedastizität konsequent robuste Standard Fehler Optionen, Clustered Standard Fehler,
VARs mit linearen Einschränkungen, Srukturelle VAR-Beschränkungsverbesserungen, VAR historische Zersetzung,
Verbesserte nichtlineare Prognose, Zusätzliche autoregressive verteilte Verzögerung (ARDL) Werkzeuge.
- Testen und Diagnostik
VAR-Strukturreste, verbesserte VAR serielle Korrelationstests, Modellschrankenprüfung.
- MIDAS-Schätzung
Eine neue Schätzmethode, die Regressionen von Daten unterschiedlicher Frequenzen erlaubt. Almon, Beta und Exponential Almon Gewichtungsschemata sind erlaubt. - FIML Schätzung mit Kovarianz Einschränkungen
Ermöglicht die Schätzung von Gleichungssystemen mittels FIML, mit Beschränkungen für die restliche Kovarianzmatrix. - Modelldruckansicht
Diese neue Ansicht erlaubt es, Gleichungen in gebrochener Form (mit numerischer Anzeige) darzustellen, ohne Verknüpfungen zu beschädigen. - Modell Szenario Beschreibungen
Fügt Beschreibungen zum Modell Szenario hinzu, diese können in die Ergebnisse exportiert werden. - Modell Szenario Ansicht
Eine übersichtlich Liste über Ihre Modell Szenarien und deren Eigenschaften - Gleichungs-Suche
Die Gleichungs-Ansicht verfügt nun über ein Suchfeld. - Modellschutz
Sie können Ihr Modell nun durch ein Passwort schützen. Benutzer die nicht über das Passwort verfügen können so nur noch das Modell betrachten, aber keine Änderungen vornehmen. - Speichern und Abrufen von Programmvariablen
Neue Funktionen für das Speichern und Laden von Programmvariablen in text-ini Dateien auf der Festplatte.
Basic Data Handling
- Numeric, alphanumeric (string), and date series; value labels.
- Extensive library of operators and statistical, mathematical, date and string functions.
- Powerful language for expression handling and transforming existing data using operators and functions.
- Samples and sample objects facilitate processing on subsets of data.
- Support for complex data structures including regular dated data, irregular dated data, cross-section data with observation identifiers, dated, and undated panel data.
- Multi-page workfiles.
- EViews native, disk-based databases provide powerful query features and integration with EViews workfiles.
- Convert data between EViews and various spreadsheet, statistical, and database formats, including (but not limited to): Microsoft Access® and Excel® files (including .XSLX and .XLSM), Gauss
Dataset files, SAS® Transport files, SPSS native and portable files, Stata
files, Tableau®, raw formatted ASCII text or binary files, HTML, or ODBC databases
and queries (ODBC support is provided only in the Enterprise Edition). - OLE support for linking EViews output, including tables and graphs, to other packages, including Microsoft Excel®, Word® and Powerpoint®.
- OLEDB support for reading EViews workfiles and databases using OLEDB-aware clients or custom programs.
- Support for FRED® (Federal Reserve Economic Data), World Bank, and EuroStat databases. Enterprise Edition support for Global Insight DRIPro and DRIBase, Haver Analytics® DLX®, FAME, EcoWin, Bloomberg®, EIA®, CEIC®, Datastream®, FactSet®, and Moody’s Economy.com databases.
- The EViews Microsoft Excel® Add-in allows you to link or import data from EViews workfiles and databases from within Excel.
- Drag-and-drop support for reading data; simply drop files into EViews for automatic conversion and linking of foreign data and metadata into EViews workfile format.
- Powerful tools for creating new workfile pages from values and dates in existing series.
- Match merge, join, append, subset, resize, sort, and reshape (stack and unstack) workfiles.
- Easy-to-use automatic frequency conversion when copying or linking data between pages of different frequency.
- Frequency conversion and match merging support dynamic updating whenever underlying data change.
- Auto-updating formula series that are automatically recalculated whenever underlying data change.
- Easy-to-use frequency conversion: simply copy or link data between pages of different frequency.
- Tools for resampling and random number generation for simulation. Random number generation for 18 different distribution functions using three different random number generators.
- Support for cloud drive access, allowing you to open and save file directly to Dropbox, OneDrive, Google Drive and Box accounts.
Time Series Data Handling
- Integrated support for handling dates and time series data (both regular and irregular).
- Support for common regular frequency data (Annual, Semi-annual, Quarterly, Monthly, Bimonthly, Fortnight, Ten-day, Weekly, Daily - 5 day week, Daily - 7 day week).
- Support for high-frequency (intraday) data, allowing for hours, minutes, and seconds frequencies. In addition, there are a number of less commonly encountered regular frequencies, including Multi-year, Bimonthly, Fortnight, Ten-Day, and Daily with an arbitrary range of days of the week.
- Specialized time series functions and operators: lags, differences, log-differences, moving averages, etc.
- Frequency conversion: various high-to-low and low-to-high methods.
- Exponential smoothing: single, double, Holt-Winters, and ETS smoothing.
- Built-in tools for whitening regression.
- Hodrick-Prescott filtering.
- Band-pass (frequency) filtering: Baxter-King, Christiano-Fitzgerald fixed length and full sample asymmetric filters.
- Seasonal adjustment: Census X-13, STL Decomposition, MoveReg, X-12-ARIMA, Tramo/Seats, moving average.
- Interpolation to fill in missing values within a series: Linear, Log-Linear, Catmull-Rom Spline, Cardinal Spline.
Statistics
Basic
- Basic data summaries; by-group summaries.
- Tests of equality: t-tests, ANOVA (balanced and unbalanced, with or without heteroskedastic variances.), Wilcoxon, Mann-Whitney, Median Chi-square, Kruskal-Wallis, van der Waerden, F-test, Siegel-Tukey, Bartlett, Levene, Brown-Forsythe.
- One-way tabulation; cross-tabulation with measures of association (Phi Coefficient, Cramer’s V, Contingency Coefficient) and independence testing (Pearson Chi-Square, Likelihood Ratio G^2).
- Covariance and correlation analysis including Pearson, Spearman rank-order, Kendall’s tau-a and tau-b and partial analysis.
- Principal components analysis including scree plots, biplots and loading plots, and weighted component score calculations.
- Factor analysis allowing computation of measures of association (including covariance and correlation), uniqueness estimates, factor loading estimates and factor scores, as well as performing estimation diagnostics and factor rotation using one of over 30 different orthogonal and oblique methods.
- Empirical Distribution Function (EDF) Tests for the Normal, Exponential, Extreme value, Logistic, Chi-square, Weibull, or Gamma distributions (Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Lilliefors, Cramer-von Mises, Anderson-Darling, Watson).
- Histograms, Frequency Polygons, Edge Frequency Polygons, Average Shifted Histograms, CDF-survivor-quantile, Quantile-Quantile, kernel density, fitted theoretical distributions, boxplots.
- Scatterplots with parametric and non-parametric regression lines (LOWESS, local polynomial), kernel regression (Nadaraya-Watson, local linear, local polynomial)., or confidence ellipses.
Time Series
- Autocorrelation, partial autocorrelation, cross-correlation, Q-statistics.
- Granger causality tests, including panel Granger causality.
- Unit root tests: Augmented Dickey-Fuller, GLS transformed Dickey-Fuller, Phillips-Perron, KPSS, Eliot-Richardson-Stock Point Optimal, Ng-Perron, as well as tests for unit roots with breakpoints.
- Cointegration tests: Johansen, Engle-Granger, Phillips-Ouliaris, Park added variables, and Hansen stability.
- Independence tests: Brock, Dechert, Scheinkman and LeBaron
- Variance ratio tests: Lo and MacKinlay, Kim wild bootstrap, Wright's rank, rank-score and sign-tests. Wald and multiple comparison variance ratio tests (Richardson and Smith, Chow and Denning).
- Long-run variance and covariance calculation: symmetric or or one-sided long-run covariances using nonparametric kernel (Newey-West 1987, Andrews 1991), parametric VARHAC (Den Haan and Levin 1997), and prewhitened kernel (Andrews and Monahan 1992) methods. In addition, EViews supports Andrews (1991) and Newey-West (1994) automatic bandwidth selection methods for kernel estimators, and information criteria based lag length selection methods for VARHAC and prewhitening estimation.
Panel and Pool
- By-group and by-period statistics and testing.
- Unit root tests: Levin-Lin-Chu, Breitung, Im-Pesaran-Shin, Fisher, Hadri.
- Cointegration tests: Pedroni, Kao, Maddala and Wu.
- Panel within series covariances and principal components.
- Dumitrescu-Hurlin (2012) panel causality tests.
- Cross-section dependence tests.
Estimation
Regression
- Linear and nonlinear ordinary least squares (multiple regression).
- Linear regression with PDLs on any number of independent variables.
- Robust regression.
- Analytic derivatives for nonlinear estimation.
- Weighted least squares.
- White and other heteroskedasticity consistent, and Newey-West robust standard errors. HAC standard errors may be computed using nonparametric kernel, parametric VARHAC, and prewhitened kernel methods, and allow for Andrews and Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection methods for kernel estimators, and information criteria based lag length selection methods for VARHAC and prewhitening estimation.
- Clustered standard errors.
- Linear quantile regression and least absolute deviations (LAD), including both Huber’s Sandwich and bootstrapping covariance calculations.
- Stepwise regression with seven different selection procedures.
- Threshold regression including TAR and SETAR, and smooth threshold regression including STAR.
- ARDL estimation, including the Bounds Test approach to cointegration.
ARMA and ARMAX
- Linear models with autoregressive moving average, seasonal autoregressive, and seasonal moving average errors.
- Nonlinear models with AR and SAR specifications.
- Estimation using the backcasting method of Box and Jenkins, conditional least squares, ML or GLS.
- Fractionally integrated ARFIMA models.
Instrumental Variables and GMM
- Linear and nonlinear two-stage least squares/instrumental variables (2SLS/IV) and Generalized Method of Moments (GMM) estimation.
- Linear and nonlinear 2SLS/IV estimation with AR and SAR errors.
- Limited Information Maximum Likelihood (LIML) and K-class estimation.
- Wide range of GMM weighting matrix specifications (White, HAC, User-provided) with control over weight matrix iteration.
- GMM estimation options include continuously updating estimation (CUE), and a host of new standard error options, including Windmeijer standard errors.
- IV/GMM specific diagnostics include Instrument Orthogonality Test, a Regressor Endogeneity Test, a Weak Instrument Test, and a GMM specific breakpoint test.
ARCH/GARCH
- GARCH(p,q), EGARCH, TARCH, Component GARCH, Power ARCH, Integrated GARCH.
- The linear or nonlinear mean equation may include ARCH and ARMA terms; both the mean and variance equations allow for exogenous variables.
- Normal, Student’s t, and Generalized Error Distributions.
- Bollerslev-Wooldridge robust standard errors.
- In- and out-of sample forecasts of the conditional variance and mean, and permanent components.
Limited Dependent Variable Models
- Binary Logit, Probit, and Gompit (Extreme Value).
- Ordered Logit, Probit, and Gompit (Extreme Value).
- Censored and truncated models with normal, logistic, and extreme value errors (Tobit, etc.).
- Count models with Poisson, negative binomial, and quasi-maximum likelihood (QML) specifications.
- Heckman Selection models.
- Huber/White robust standard errors.
- Count models support generalized linear model or QML standard errors.
- Hosmer-Lemeshow and Andrews Goodness-of-Fit testing for binary models.
- Easily save results (including generalized residuals and gradients) to new EViews objects for further analysis.
- General GLM estimation engine may be used to estimate several of these models, with the option to include robust covariances.
Panel Data/Pooled Time Series, Cross-Sectional Data
- Linear and nonlinear estimation with additive cross-section and period fixed or random effects.
- Choice of quadratic unbiased estimators (QUEs) for component variances in random effects models: Swamy-Arora, Wallace-Hussain, Wansbeek-Kapteyn.
- 2SLS/IV estimation with cross-section and period fixed or random effects.
- Estimation with AR errors using nonlinear least squares on a transformed specification
- Generalized least squares, generalized 2SLS/IV estimation, GMM estimation allowing for cross-section or period heteroskedastic and correlated specifications.
- Linear dynamic panel data estimation using first differences or orthogonal deviations with period-specific predetermined instruments (Arellano-Bond).
- Panel serial correlation tests (Arellano-Bond).
- Robust standard error calculations include seven types of robust White and Panel-corrected standard errors (PCSE).
- Testing of coefficient restrictions, omitted and redundant variables, Hausman test for correlated random effects.
- Panel unit root tests: Levin-Lin-Chu, Breitung, Im-Pesaran-Shin, Fisher-type tests using ADF and PP tests (Maddala-Wu, Choi), Hadri.
- Panel cointegration estimation: Fully Modified OLS (FMOLS, Pedroni 2000) or Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares (DOLS, Kao and Chaing 2000, Mark and Sul 2003).
- Pooled Mean Group (PMG) estimation.
Generalized Linear Models
- Normal, Poisson, Binomial, Negative Binomial, Gamma, Inverse Gaussian, Exponential Mena, Power Mean, Binomial Squared families.
- Identity, log, log-complement, logit, probit, log-log, complimentary log-log, inverse, power, power odds ratio, Box-Cox, Box-Cox odds ratio link functions.
- Prior variance and frequency weighting.
- Fixed, Pearson Chi-Sq, deviance, and user-specified dispersion specifications. Support for QML estimation and testing.
- Quadratic Hill Climbing, Newton-Raphson, IRLS - Fisher Scoring, and BHHH estimation algorithms.
- Ordinary coefficient covariances computed using expected or observed Hessian or the outer product of the gradients. Robust covariance estimates using GLM, HAC, or Huber/White methods.
Single Equation Cointegrating Regression
- Support for three fully efficient estimation methods, Fully Modified OLS (Phillips and Hansen 1992), Canonical Cointegrating Regression (Park 1992), and Dynamic OLS (Saikkonen 1992, Stock and Watson 1993
- Engle and Granger (1987) and Phillips and Ouliaris (1990) residual-based tests, Hansen's (1992b) instability test, and Park's (1992) added variables test.
- Flexible specification of the trend and deterministic regressors in the equation and cointegrating regressors specification.
- Fully featured estimation of long-run variances for FMOLS and CCR.
- Automatic or fixed lag selection for DOLS lags and leads and for long-run variance whitening regression.
- Rescaled OLS and robust standard error calculations for DOLS.
User-specified Maximum Likelihood
- Use standard EViews series expressions to describe the log likelihood contributions.
- Examples for multinomial and conditional logit, Box-Cox transformation models, disequilibrium switching models, probit models with heteroskedastic errors, nested logit, Heckman sample selection, and Weibull hazard models.
Systems of Equations
Basic
- Linear and nonlinear estimation.
- Least squares, 2SLS, equation weighted estimation, Seemingly Unrelated Regression, and Three-Stage Least Squares.
- GMM with White and HAC weighting matrices.
- AR estimation using nonlinear least squares on a transformed specification.
- Full Information Maximum Likelihood (FIML).
VAR/VEC
- Estimate structural factorizations in VARs by imposing short- or long-run restrictions, or both.
- Bayesian VARs.
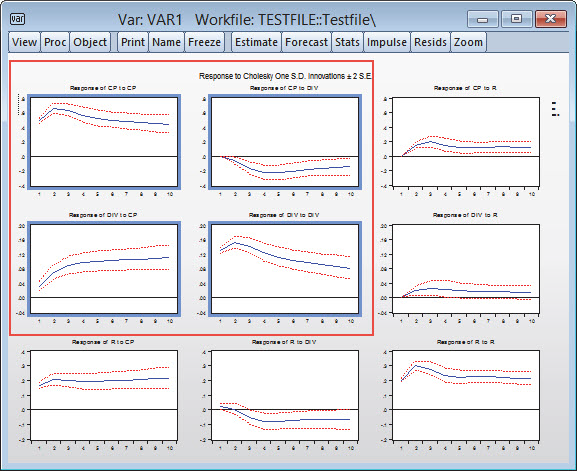
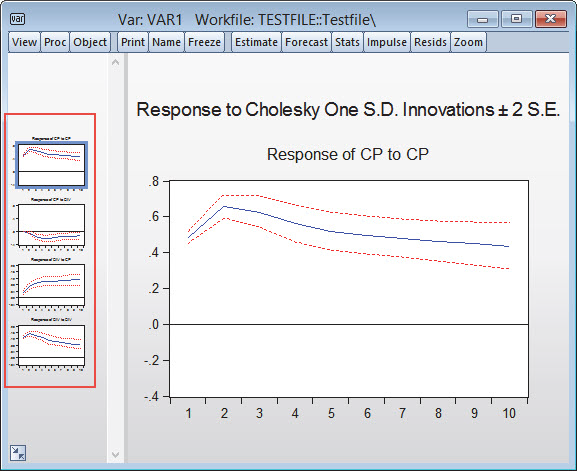
- Impulse response functions in various tabular and graphical formats with standard errors calculated analytically or by Monte Carlo methods.
- Impulse response shocks computed from Cholesky factorization, one-unit or one-standard deviation residuals (ignoring correlations), generalized impulses, structural factorization, or a user-specified vector/matrix form.
- Historical decomposition of standard VAR models.
- Impose and test linear restrictions on the cointegrating relations and/or adjustment coefficients in VEC models.
- View or generate cointegrating relations from estimated VEC models.
- Extensive diagnostics including: Granger causality tests, joint lag exclusion tests, lag length criteria evaluation, correlograms, autocorrelation, normality and heteroskedasticity testing, cointegration testing, other multivariate diagnostics.
Multivariate ARCH
- Conditional Constant Correlation (p,q), Diagonal VECH (p,q), Diagonal BEKK (p,q), with asymmetric terms.
- Extensive parameterization choice for the Diagonal VECH's coefficient matrix.
- Exogenous variables allowed in the mean and variance equations; nonlinear and AR terms allowed in the mean equations.
- Bollerslev-Wooldridge robust standard errors.
- Normal or Student's t multivariate error distribution
- A choice of analytic or (fast or slow) numeric derivatives. (Analytics derivatives not available for some complex models.)
- Generate covariance, variance, or correlation in various tabular and graphical formats from estimated ARCH models.
State Space
- Kalman filter algorithm for estimating user-specified single- and multiequation structural models.
- Exogenous variables in the state equation and fully parameterized variance specifications.
- Generate one-step ahead, filtered, or smoothed signals, states, and errors.
- Examples include time-varying parameter, multivariate ARMA, and quasilikelihood stochastic volatility models.
Testing and Evaluation
- Actual, fitted, residual plots.
- Wald tests for linear and nonlinear coefficient restrictions; confidence ellipses showing the joint confidence region of any two functions of estimated parameters.
- Other coefficient diagnostics: standardized coefficients and coefficient elasticities, confidence intervals, variance inflation factors, coefficient variance decompositions.
- Omitted and redundant variables LR tests, residual and squared residual correlograms and Q-statistics, residual serial correlation and ARCH LM tests.
- White, Breusch-Pagan, Godfrey, Harvey and Glejser heteroskedasticity tests.
- Stability diagnostics: Chow breakpoint and forecast tests, Quandt-Andrews unknown breakpoint test, Bai-Perron breakpoint tests, Ramsey RESET tests, OLS recursive estimation, influence statistics, leverage plots.
- ARMA equation diagnostics: graphs or tables of the inverse roots of the AR and/or MA characteristic polynomial, compare the theoretical (estimated) autocorrelation pattern with the actual correlation pattern for the structural residuals, display the ARMA impulse response to an innovation shock and the ARMA frequency spectrum.
- Easily save results (coefficients, coefficient covariance matrices, residuals, gradients, etc.) to EViews objects for further analysis.
See also Estimation and Systems of Equations for additional specialized testing procedures.
Forecasting and Simulation
- In- or out-of-sample static or dynamic forecasting from estimated equation objects with calculation of the standard error of the forecast.
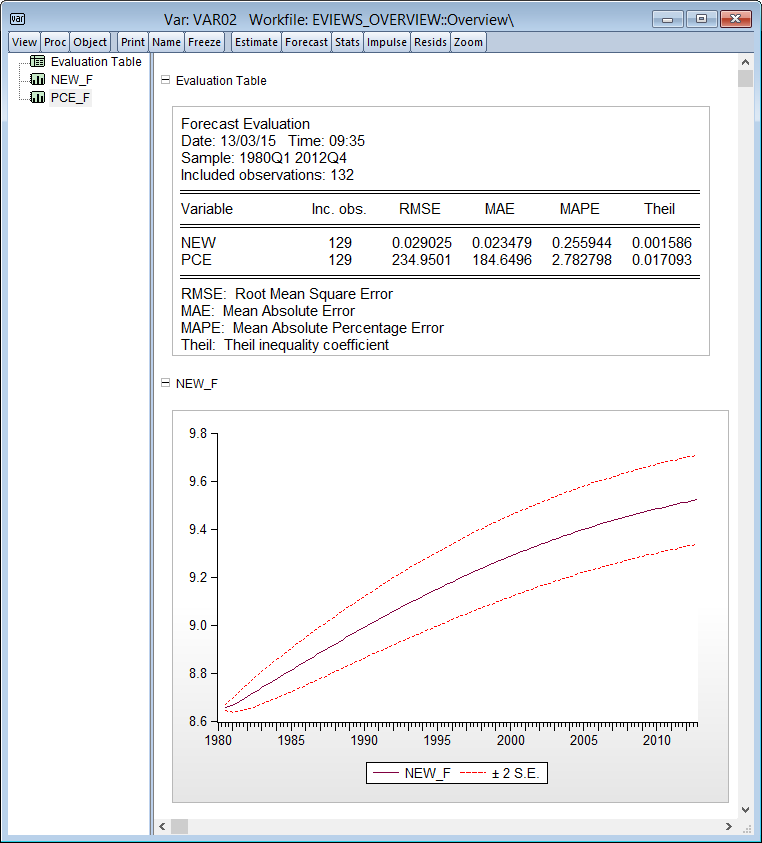
- Forecast graphs and in-sample forecast evaluation: RMSE, MAE, MAPE, Theil Inequality Coefficient and proportions
- State-of-the-art model building tools for multiple equation forecasting and multivariate simulation.
- Model equations may be entered in text or as links for automatic updating on re-estimation.
- Display dependency structure or endogenous and exogenous variables of your equations.
- Gauss-Seidel, Broyden and Newton model solvers for non-stochastic and stochastic simulation. Non-stochastic forward solution solve for model consistent expectations. Stochasitc simulation can use bootstrapped residuals.
- Solve control problems so that endogenous variable achieves a user-specified target.
- Sophisticated equation normalization, add factor and override support.
- Manage and compare multiple solution scenarios involving various sets of assumptions.
- Built-in model views and procedures display simulation results in graphical or tabular form.
Graphs and Tables
- Line, dot plot, area, bar, spike, seasonal, pie, xy-line, scatterplots, bubbleplots, boxplots, error bar, high-low-open-close, and area band.
- Powerful, easy-to-use categorical and summary graphs.
- Auto-updating graphs which update as underlying data change.
- Observation info and value display when you hover the cursor over a point in the graph.
- Histograms, average shifted historgrams, frequency polyons, edge frequency polygons, boxplots, kernel density, fitted theoretical distributions, boxplots, CDF, survivor, quantile, quantile-quantile.
- Scatterplots with any combination parametric and nonparametric kernel (Nadaraya-Watson, local linear, local polynomial) and nearest neighbor (LOWESS) regression lines, or confidence ellipses.
- Interactive point-and-click or command-based customization.
- Extensive customization of graph background, frame, legends, axes, scaling, lines, symbols, text, shading, fading, with improved graph template features.
- Table customization with control over cell font face, size, and color, cell background color and borders, merging, and annotation.
- Copy-and-paste graphs into other Windows applications, or save graphs as Windows regular or enhanced metafiles, encapsulated PostScript files, bitmaps, GIFs, PNGs or JPGs.
- Copy-and-paste tables to another application or save to an RTF, HTML, LaTeX, PDF, or text file.
- Manage graphs and tables together in a spool object that lets you display multiple results and analyses in one object
Commands and Programming
- Object-oriented command language provides access to menu items.
- Batch execution of commands in program files.
- Looping and condition branching, subroutine, and macro processing.
- String and string vector objects for string processing. Extensive library of string and string list functions.
- Extensive matrix support: matrix manipulation, multiplication, inversion, Kronecker products, eigenvalue solution, and singular value decomposition.
External Interface and Add-Ins
- EViews COM automation server support so that external programs or scripts can launch or control EViews, transfer data, and execute EViews commands.
- EViews offers COM Automation client support application for MATLAB® and R so that EViews may be used to launch or control the application, transfer data, or execute commands.
- The EViews Microsoft Excel® Add-in offers a simple interface for fetching and linking from within Microsoft Excel® (2000 and later) to series and matrix objects stored in EViews workfiles and databases.
- The EViews Add-ins infrastructure offers seamless access to user-defined programs using the standard EViews command, menu, and object interface.
- Download and install predefined Add-ins from the EViews website.